Flume
...大约 10 分钟
Flume
一、写flume的步骤
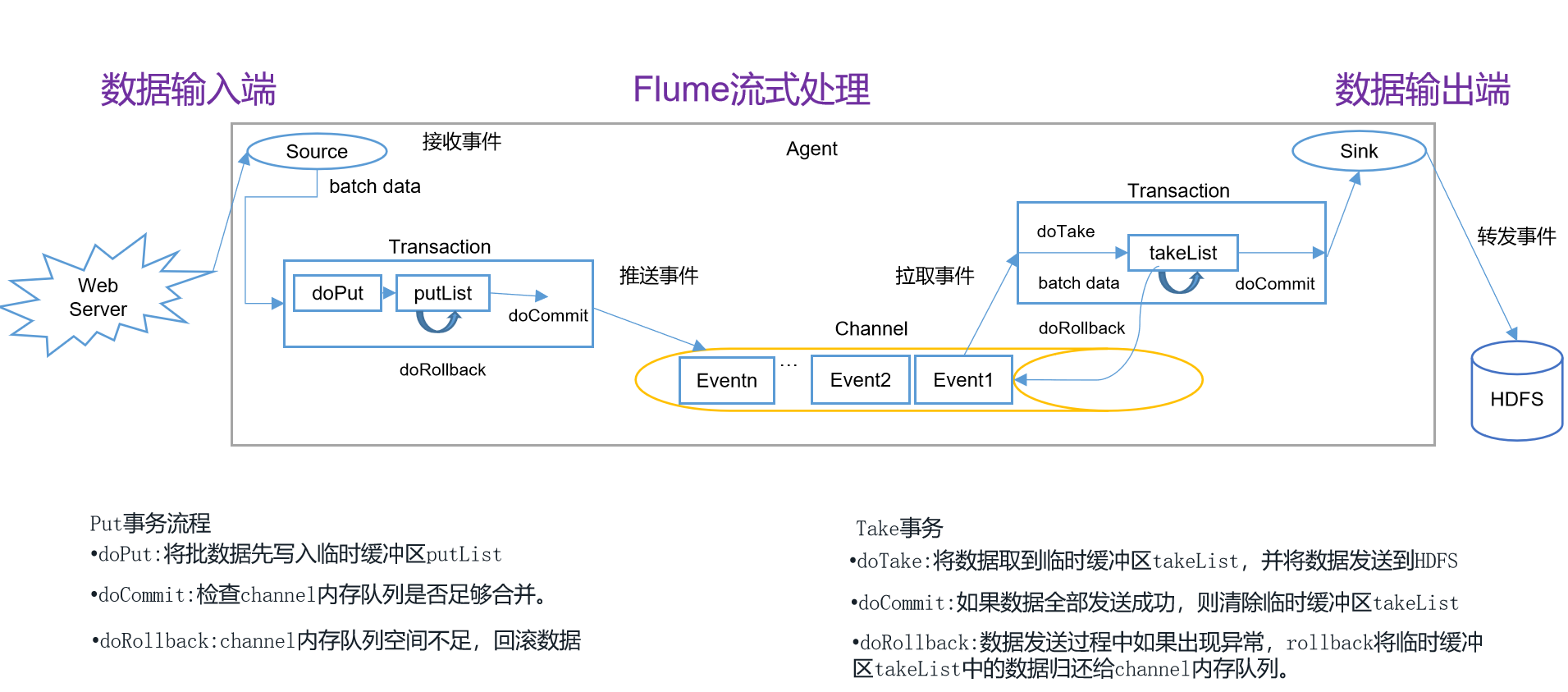
1.0.0 Flume 事务
1.0.1 Flume Agent内部原理
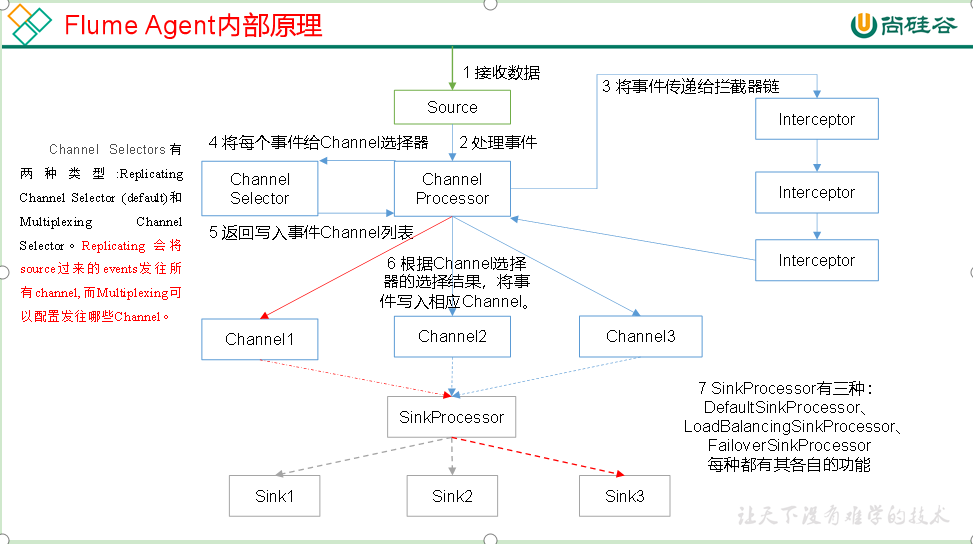 图1
图1
1.1 画拓扑图
总结:一个channel只能输出一个结果文件。
一个flume agent 由 source + channel + sink 构成,类比于mapper + shuffer + reducer。
1.1.1 确定source类型
常用类型:
1) arvo: 用于Flume agent 之间的数据源传递
2) netcat: 用于监听端口
3)exec: 用于执行linux中的操作指令
4) spooldir: 用于监视文件或目录
5) taildir: 用于监视文件或目录,同时支持追加的监听
总结 ,3/4/5三种方式,最常用的是5,适合用于监听多个实时追加的文件,并且能够实现断点续传。1.1.2 确定channel selector 的选择器
1)replicating channel selector:复制,每个channel发一份数据 -- 默认的选择器
2) multiplexing channel selector : 根据配置配件,指定source源获取的数据发往一个或多个channel1.1.3 确认channel类型参数
1) Memory Channel : 加载在内存中,存在数据丢失的风险 -- 学习阶段使用此参数
2) File Channel :落入磁盘1.1.4 确定sinkprocessor参数
1) DefaultSinkProcessor:对应的是单个的Sink
2) LoadBalancingSinkProcessor :对应的是多个的Sink,可以实现负载均衡的功能
3) FailoverSinkProcessor :对应的是多个的Sink,容错功能,先指定一个sink,所有的数据都走指定的sink,当sink故障以后,其他的sink顶上,如果开始sink恢复了,那么数据继续走原有指定的sink。1.1.5 确定sink的类型
常使用的类型有:
1) avro: 用于输出到下一个Flume Agent ,一个开源的序列化框架
2) hdfs: 输出到hdfs
3) fill_roll: 输出到本地
4) logger: 输出到控制台
5) hbase: 输出到hbase1.1.6 拓扑例图
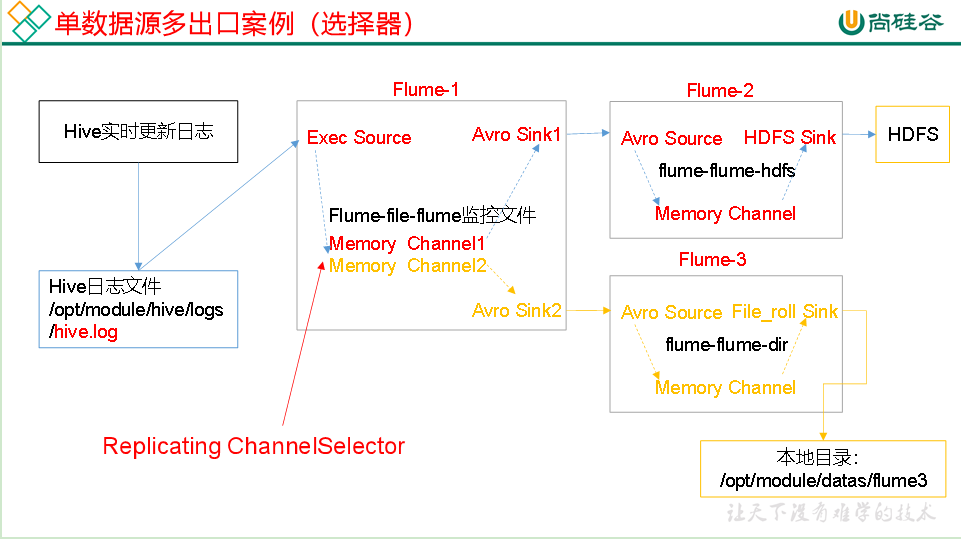
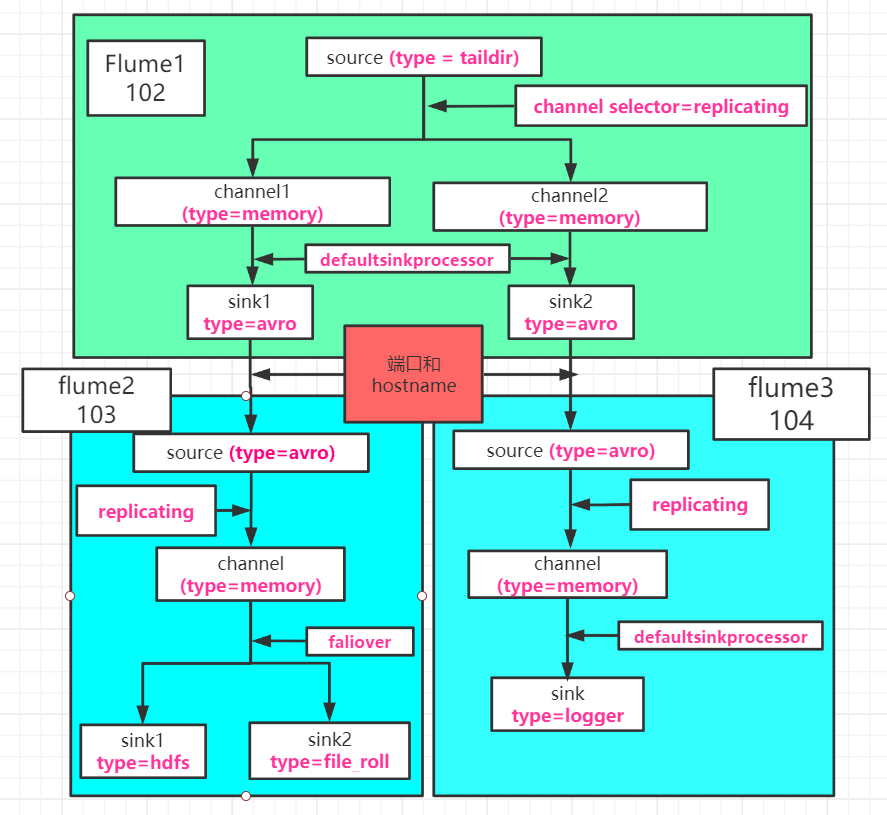
图3
1.2 写配置文件
1.2.1 配置文件的构成
- Name the components on this agent -- agent Name
- Describe/configure the source -- source
- channel selector
- Describe the channel -- channel
- sinkprocessor
- Describe the sink --sink
- Bind the source and sink to the channel -- 连接source、channel、sink
1.2.2 agent Name
情况1:source、channel、sink各一个
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1情况2:source一个、channel一个、sink多个
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinks = k1 k2情况3:source一个、channel多个、sink多个
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c21.2.3 source
情况1:avro
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102 -- hosename
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141 -- 端口号情况2:netcat
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost -- 指接收来自ip为localhost发来的数据,如果是0.0.0.0,则表示可以接收来自任意ip地址发来的数据
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 -- 本机的端口号,从该端口接收数据情况3:exec
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log -->linux执行的命令
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c -- linux的解析器情况4: sqooldir
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = spooldir -- 定义source类型
a1.sources.r1.spoolDir = /opt/module/flume/upload -- 定义监控的文件或目录
a1.sources.r1.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED -- 定义文件上传后的后缀
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true -- 是否有文件头
#忽略所有以.tmp结尾的文件,不上传
a1.sources.r1.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*\.tmp)情况5:talidir
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/module/flume/tail_dir.json -- 指定position_file 的位置,(记录每次上传后的偏移量,实现断点续传的关键)
a1.sources.r1.batchSize=500
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 f2 -- 监控的文件目录集合
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /opt/module/flume/files/.*file.* -- 定义监控的文件目录1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f2 = /opt/module/flume/files/.*log.* -- 定义监控的文件目录21.2.4 channel selector
情况1: replicating channel selector
# 将数据流复制给所有channel
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating情况2:multiplexing channel selector 需配合指定的拦截器使用(interceptor)
-- 指定拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 -- 指定拦截器的名称
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.atguigu.flume.interceptor.CustomInterceptor$Builder
-- 指定拦截器的类型 = 自定义拦截器中builder的实现类的全类名
-- 指定channel的选择器
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing -- 定义channel的选择器类型
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type -- 自定义拦截器的header的k
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.letter = c1 -- letter是map中一个value值,相同的letter进入一个channel中
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.number = c2 -- number是map中一个value值,相同的number进入一个channel中1.2.5 channel
情况1: memory
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 --表示channel总容量为1000个event
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 -- 表示channel传输时收集到的100条event情况2 : flie
a1.channels.c1.type=file --channel类型
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir=/opt/module/flume/checkpoint/behavior1 --checkpoint文件存储的地址
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs=/opt/module/flume/data/behavior1/ -- channel中event文件在磁盘中存储的地址
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000000 --checkpoint个数的最大容量
a1.channels.c1.maxFileSize=2146435071 --一个event文件存储的最大的大小
a1.channels.c1.keep-alive=6 --当put事务将数据提交到channel队列中,channel队列没有足够的空间时,提交事务等待的最大时间1.2.6 sinkprocessor
情况1:DefaultSinkProcessor --对应单个Sink
不用写任何配置信息,默认值。情况2:FailoverSinkProcessor --对应的是Sink Group
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover -- 指定类型
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5 --设置K1的sink的优先级
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10 --设置K2的sink的优先级
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000 -- 设置故障的转换时间10s。默认值为30s情况3:LoadBalancingSinkProcessor --对应的是Sink Group
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type =load_balance -- 指定类型
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true -- 暂不讨论
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector =round_robin -- 暂不讨论1.2.7 sink
情况1:avro
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop104 -- hosaname
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 -- 端口情况2:hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9820/flume/upload2/%Y%m%d/%H -- 上传到HDFS的路径
#上传文件的前缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = upload-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60 -- 单位是秒
#设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是128M
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0情况3:fill_roll
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a1.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/module/flume/datas/flume3 -- 指定上传到本地的路径情况4:logger
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger情况5:hbase ---暂时不讨论
1.2.8 连接source、channel、sink
情况1:source、channel、sink各一个、
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1情况2:source一个、channel一个、sink多个
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1情况3:source一个、channel多个、sink多个
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2 --特别注意channel没有“s”1.2.9 端口和ip的区别
- sink端:向指定ip地址的端口发送数据
端口:
ip(hostname):- source端:监视指定端口并接收指定ip发送来的数据
端口:该端口只能是自己机器的端口
ip(hostname):指能够接受来自此ip的数据1.3 连接flume
1.3.1 查看指定ip的通信端口
sudo netstat -ntlp | grep 端口号1.3.2 关闭端口
sudo kill 端口的进程号1.3.3 连接指定ip地址的指定端口
nc ip 端口号1.3.4 启动flume
bin/flume-ng agent -n [agent name] -c conf -f [自定义flume配置文件] -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console二、自定义interceptor,source、 sink
2.1 自定义intercepor
package flume_interceptor;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author lianzhipeng
* @Description
* @create 2020-05-05 10:45
*/
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
/**
* Description: 初始化方法,新建Interceptor时使用
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 10:45
* @return: void
*/
public void initialize() {
}
/**
* Description: 更改方法,对event进行处理
*
* @param event 传入的数据
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 10:47
* @return: org.apache.flume.Event 返回处理好的数据
*/
public Event intercept(Event event) {
//获取event的header
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
//获取event的body
byte[] body = event.getBody();
//处理数据
String string = new String(body);
char c = string.charAt(0);
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' || c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {
headers.put("type", "char");
} else {
headers.put("type", "not-char");
}
//返回数据
return event;
}
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> list) {
for (Event event : list) {
intercept(event);
}
return list;
}
public void close() {
}
/**
* 框架会调用MyBulider来创建自定义拦截器实例
*/
public static class MyBulider implements Builder {
/**
* Description: 创建自定义拦截器实例的方法
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 10:54
* @return: org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor
*/
public Interceptor build() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
/**
* Description: 读取配置信息
*
* @param context
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 10:54
* @return: void
*/
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}2.2 自定义source
package flume_interceptor;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.channel.ChannelProcessor;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
/**
* @author lianzhipeng
* @Description
* @create 2020-05-05 14:31
*/
public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
private String prefix;
private Long interval;
/**
* Description:拉取事件并交给ChannelProcessor处理的方法
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 14:33
* @return: org.apache.flume.PollableSource.Status
*/
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status status = null;
try {
// 通过外部方法拉取数据
Event e = getSomeData();
// Store the Event into this Source's associated Channel(s)
ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = getChannelProcessor();
channelProcessor.processEvent(e);
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Log exception, handle individual exceptions as needed
status = Status.BACKOFF;
// re-throw all Errors
if (t instanceof Error) {
throw (Error)t;
}
}
return status;
}
/**
* Description:拉取数据并包装成event的过程
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 14:55
* @return: org.apache.flume.Event 拉取到的数据
*/
private Event getSomeData() throws InterruptedException {
int i = (int) (Math.random() * 1000);
//添加前缀
String message = prefix + i ;
Thread.sleep(interval);
//
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
event.setBody(message.getBytes());
return event;
}
/**
* Description: 如果拉取不到数据,backoff时间的增长速度
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 14:34
* @return: long 增长量
*/
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 1000;
}
/**
* Description: 最大的等待时间
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 14:38
* @return: long
*/
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 10000;
}
/**
* Description:配置参数,来自于configurable,可以定义我们自己定义的source
*
* @param context 配置文件
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 14:39
* @return: void
*/
public void configure(Context context) {
prefix = context.getString("prefff","xxxx" );
interval = context.getLong("interval",500L);
}
}2.3 自定义sink
package flume_interceptor;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author lianzhipeng
* @Description
* @create 2020-05-05 14:31
*/
public class MySiink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
/**
* Description: 改方法调用时,会从Channel中拉取数据并处理
*
* @Author: lianzhipeng
* @Date: 2020/5/5 15:09
* @return: org.apache.flume.Sink.Status 处理的状态
*/
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status status = null;
// Start transaction
//获取channel
Channel ch = getChannel();
//拉取数据的事务
Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction();
//开始拉取
txn.begin();
try {
// This try clause includes whatever Channel operations you want to do
//拉取的数据,如果拉取不到,则返回null
Event event;
//如果拉取的数据为null,则等0.1秒后继续拉取数据,知道拉取数据
while ((event = ch.take()) == null) {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
// Send the Event to the external repository.
//如果拉取到了数据,将数据进行处理
storeSomeData(event);
txn.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Throwable t) {
txn.rollback();
// Log exception, handle individual exceptions as needed
status = Status.BACKOFF;
// re-throw all Errors
if (t instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) t;
}
} finally {
//拉取事务的关闭
txn.close();
}
return status;
}
private void storeSomeData(Event event) throws IOException {
//获取event的body数据
byte[] body = event.getBody();
//将数据写出到控制台
System.out.write(body);
System.out.println();
}
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}三、kafka与flume的结合
kafka:数据的中转站,主要功能由topic体现;
flume:数据的采集,通过source和sink体现。
3.1 kafka source
-- 问题 :
fulme在kafka中的作用
-- 答案:
消费者配置文件:
a1.sources.r1.type = org.apache.flume.source.kafka.KafkaSource --source类型
a1.sources.r1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoop105:9092,hadoop106:9092 -- kafka的集群
a1.sources.r1.kafka.topics=topic_log -- 订阅的话题
a1.sources.r1.batchSize=6000 --putlist中数据达到了6K以后提交到channel中
a1.sources.r1.batchDurationMillis=2000 --拉取数据的时间达到2s以后,将获取的数据提交到channel中3.2 kakfa channel
- kakfa channel这种情况使用的最多,此时的flume可以是消费者、生产者、source和sink之间的缓冲区(具有高吞吐量的优势),Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。
- 一共有三种情况,分别是:
-- 情况一: 有Flume source and sink -- 缓冲区
kakfa channel为事件提供了可靠且高可用的通道;
-- 情况二: 有source and interceptor but no sink --生产者
it allows writing Flume events into a Kafka topic, for use by other app
-- 情况三: 有 sink, but no source --消费者
it is a low-latency, fault tolerant way to send events from Kafka to Flume sinks such as HDFS, HBase or Solr配置文件:
a1.channels.c1.type = org.apache.flume.channel.kafka.KafkaChannel ----channel类型
a1.channels.c1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoop105:9092,hadoop106:9092,hadoop107:9092 --kafka集群
a1.channels.c1.kafka.topic =topic_log --话题
a1.channels.c1.parseAsFlumeEvent=false --不需要event的header数据3.3 kafka sink
作用:将数据拉取到kafka的topic中。
配置文件:
a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink --sink类型
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.topic =topic_log --话题
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoop105:9092,hadoop106:9092,hadoop107:9092 --kafka集群
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.flumeBatchSize = 20
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.acks = 1 --副本策略
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.linger.ms = 1
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.compression.type = snappy --压缩格式 赞助





